Amazon AppSec CTF: HalCrypto
Executive Summary
- Challenge: HalCrypto
- Category: Web Security
- Vulnerability: JWT validation bypass via URL confusion with @ symbol
- Impact: Authentication bypass leading to admin access
- Flag:
HTB{r3d1r3c73d_70_my_s3cr37s}
Vulnerability Overview
Attack Flow Diagram
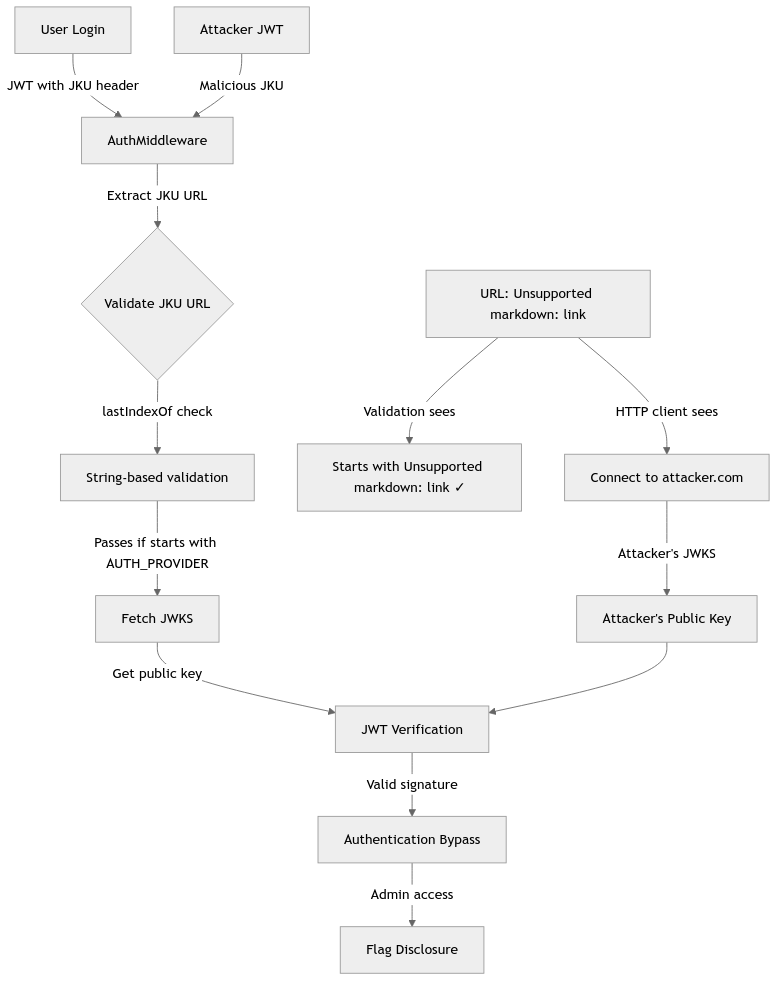
Source-to-Sink Analysis
1. Entry Point - JWT Authentication (Source)
The vulnerability starts when the AuthMiddleware processes JWT tokens:
// middleware/AuthMiddleware.js:5-34
module.exports = async (req, res, next) => {
try {
if (req.cookies.session === undefined) {
if (!req.is('application/json')) return res.redirect('/');
return res.status(401).send(response('Authentication required!'));
}
return JWTHelper.getHeader(req.cookies.session)
.then(header => {
if (header.jku && header.kid) {
// VULNERABILITY: Weak URL validation using lastIndexOf
if (header.jku.lastIndexOf(config.AUTH_PROVIDER, 0) !== 0) {
return res.status(500).send(response('The JWKS endpoint is not from localhost!'));
}
return JWTHelper.getPublicKey(header.jku, header.kid)
.then(pubkey => {
return JWTHelper.verify(req.cookies.session, pubkey)
.then(data => {
req.user = data.user;
return next();
})
.catch(() => res.status(403).send(response('Authentication token could not be verified!')));
})
.catch(() => res.redirect('/logout'));
}
return res.status(500).send(response('Missing required claims in JWT!'));
})
.catch(err => res.status(500).send(response("Invalid session token supplied!")));
} catch (e) {
return res.status(500).send(response(e.toString()));
}
}
2. The Vulnerable Validation - String-based URL Check
The critical vulnerability lies in line 14 of AuthMiddleware.js: